📊🚀 Power BI in the Age of Fabric, Automation, and Intelligent Analytics🤖📈
As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, Power BI continues to evolve beyond traditional reporting. This session provided a deep dive into Power BI reporting, sharing, automation, and AI integration, with a strong focus on Microsoft Fabric, data refresh strategies, and next-generation tools like MCP Servers.
🔗 Publishing & Sharing Power BI Reports with Microsoft Fabric
The session began with an overview of how Power BI reports are published and shared using Microsoft Fabric. While Power BI Desktop remains free for report creation, collaboration and online sharing require a Fabric subscription.
Participants explored:
Publishing reports from Power BI Desktop to Fabric
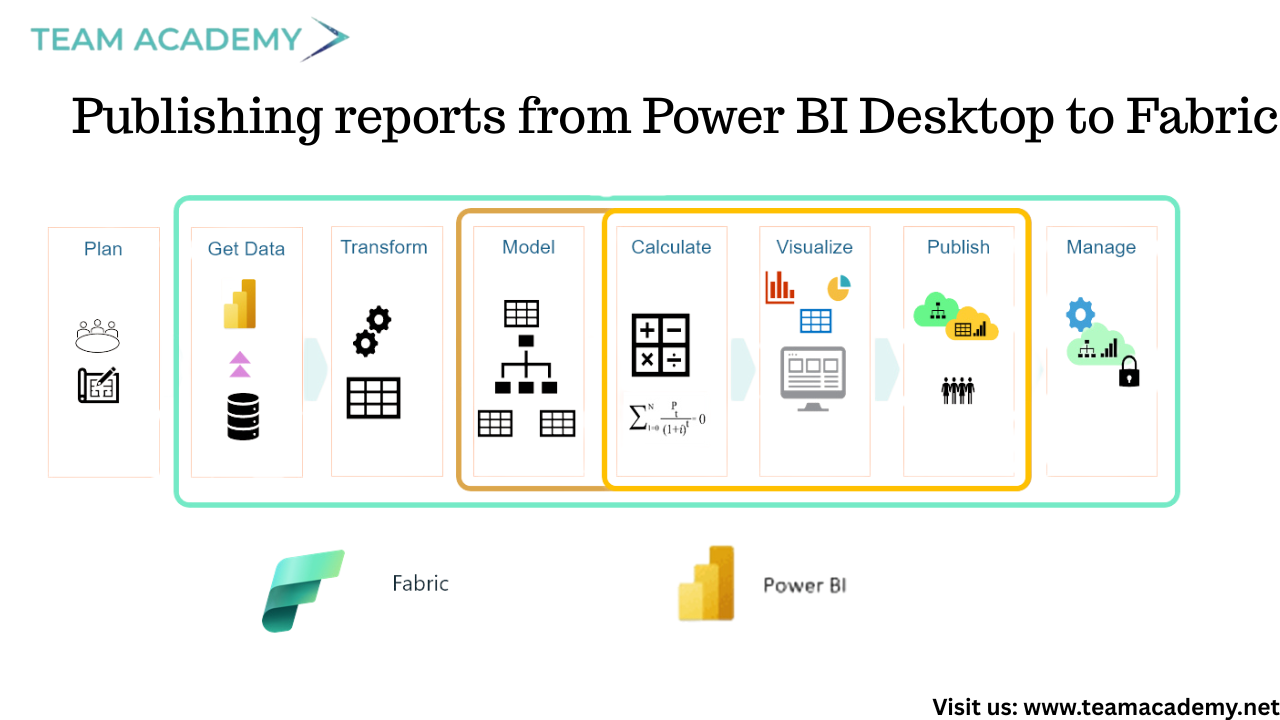
Sharing reports via Microsoft Teams and web embedding
Exporting reports as PDFs
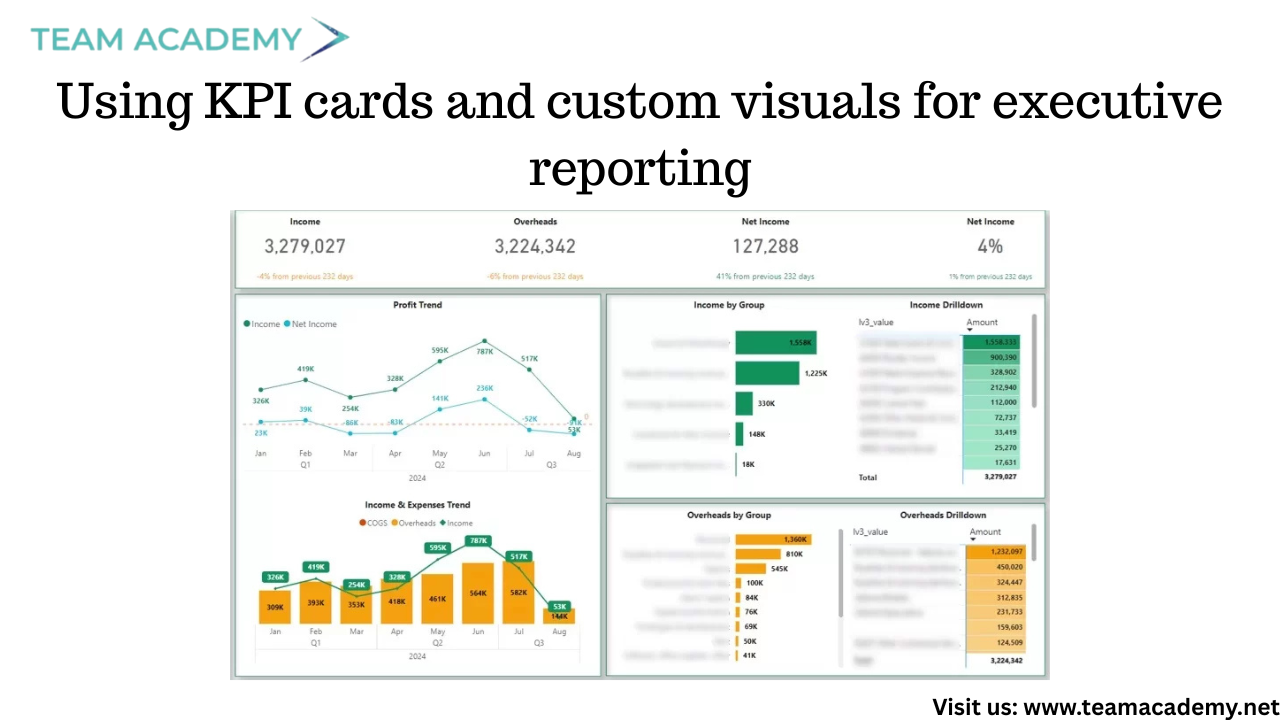
Using KPI cards and custom visuals for executive reporting
Fabric was positioned as the future of Power BI collaboration, replacing traditional Power BI Service workflows with richer sharing and governance capabilities.
🔄 Data Refresh, Semantic Models & Real-Time Reporting
A key discussion centered on data refresh mechanisms and how Power BI handles real-time or scheduled updates. It was clarified that refresh behavior depends on:
Data source type (SQL, APIs, cloud systems)
Gateway configuration
Semantic models within Fabric
Participants learned how semantic models allow interactive dashboards, enable exports to Excel, and support advanced analytics across multiple connected data sources.
🔔 Alerts, KPIs & Automated Notifications

The session highlighted Power BI’s alerting capabilities, showing how users can:
Configure KPI thresholds
Receive automatic alerts via Teams and Outlook
Monitor performance without manually opening dashboards
This feature was emphasized as especially valuable for operational teams and leadership monitoring critical business metrics.
🤖 AI Features in Power BI: Data Agents & Smart Analytics
Power BI’s AI evolution took center stage with an introduction to:
Data Agents (AI chatbots for Power BI reports – preview feature)
Natural language querying of dashboards
AI-assisted insights without manual analysis
These tools aim to reduce dependency on complex queries while improving accessibility for non-technical users.
🧠 MCP Server: Power BI Meets AI Automation
One of the most impactful segments focused on MCP (Model Context Protocol) Server integration with Visual Studio Code.
Key capabilities demonstrated:
Auto-generation of DAX measures using natural language
Organizing and documenting Power BI data models
Reducing manual DAX coding effort
Creating Word documentation directly from Power BI models
Participants were guided step-by-step through:
Installing Visual Studio Code
Enabling GitHub Copilot Chat
Installing the Power BI Modeling MCP Server
Connecting MCP Server to Power BI datasets
Despite minor setup challenges, the overall process was shown to be fast and highly beneficial for analysts and developers.
🎓 Exam Preparation & What’s Next
The session concluded with discussions around PL300 exam preparation, highlighting the importance of:
Practicing with mock exams
Reviewing official Microsoft learning resources
Using LMS materials for structured revision
Looking ahead, upcoming sessions will expand into Power Automate, Power Apps, and deeper AI-driven integrations—paving the way for a fully automated analytics ecosystem.
✨ Key Takeaways
✅ Microsoft Fabric is the future of Power BI collaboration
✅ Semantic models enable smarter, scalable reporting
✅ AI features reduce complexity and speed up analysis
✅ MCP Servers revolutionize DAX and data modeling
✅ Power BI skills now extend beyond visualization into automation