🛡️ Patient Safety in Healthcare: Preventing Errors, Managing Risks, and Saving Lives
🌍 Introduction
Patient safety is a critical pillar of healthcare quality. This session provided an in-depth exploration of patient safety concepts, focusing on how medical errors occur, how risks can be reduced, and how healthcare systems can be designed to protect patients from harm. Through real-world examples and proven frameworks, participants were encouraged to think beyond individual mistakes and focus on system-wide safety improvements.
⚠️ Understanding Medical Errors and Adverse Events
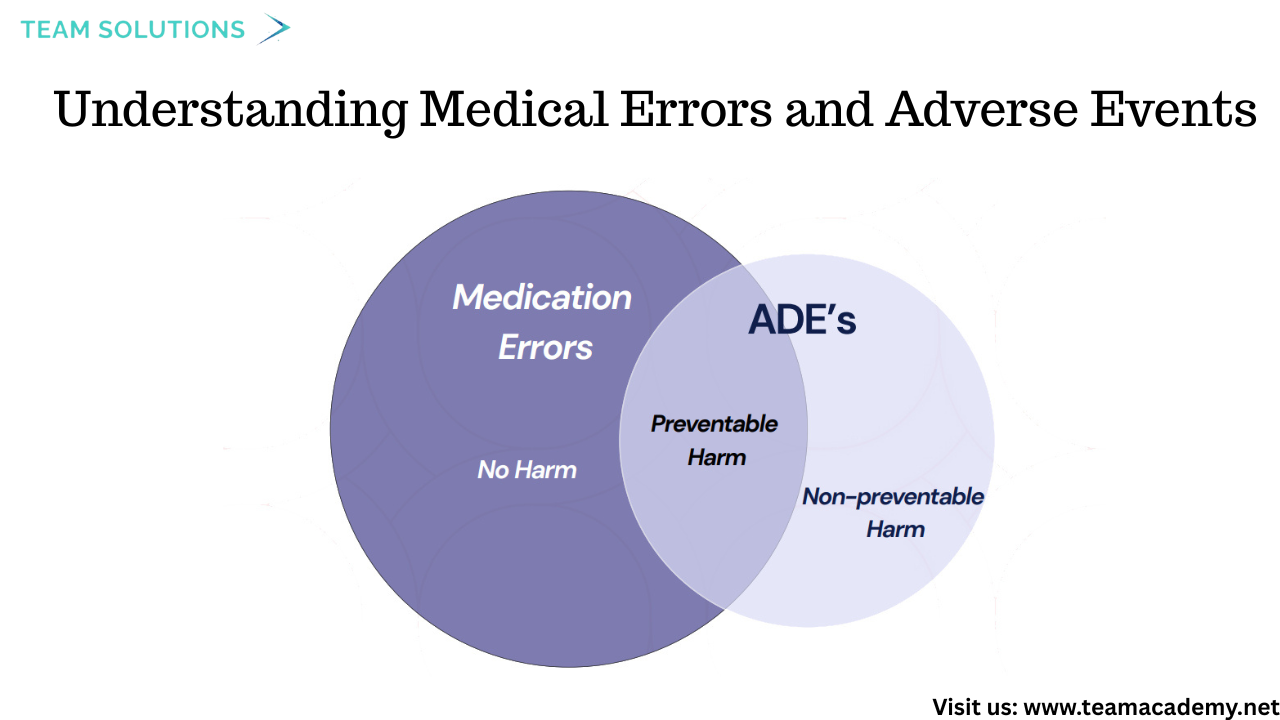
The discussion began with defining medical errors as failures of planned actions or the use of incorrect plans. These were categorized into:
❌ Preventable adverse events
⚠️ Non-preventable adverse events
🚨 Adverse events due to negligence
Special attention was given to near-miss events and close calls, where harm was avoided but could have occurred. These events were highlighted as valuable learning opportunities rather than incidents to hide.
🧀 Swiss Cheese Theory: Why Errors Happen
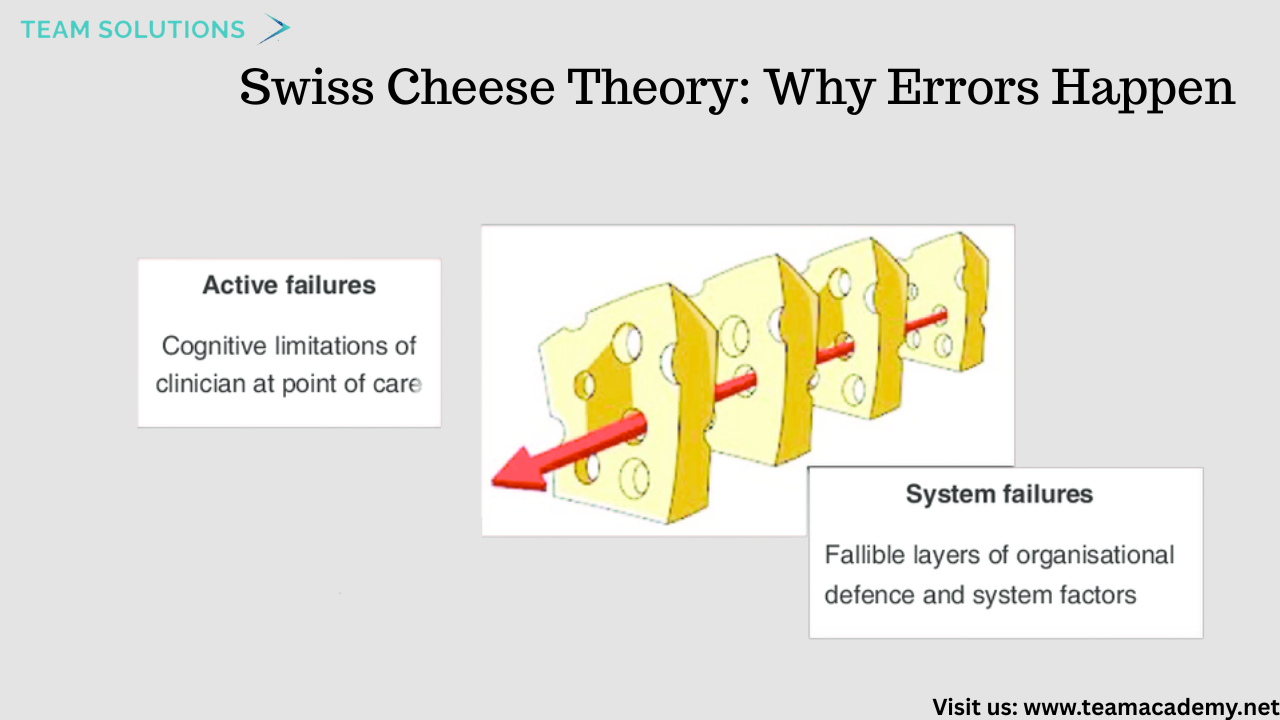
One of the key models discussed was the Swiss Cheese Theory, which explains how patient harm occurs when multiple safety barriers fail at the same time.
🔪 Active failures (Sharp End): Errors made by frontline staff
🧱 Latent failures (Blunt End): Systemic weaknesses such as poor policies, inadequate training, or flawed processes
The session emphasized that improving patient safety requires addressing both human errors and system design flaws.
🚧 Hazards vs Risks in Healthcare
Participants explored the difference between hazards and risks using simple but powerful examples:
🦈 A hazard exists (e.g., infection risk), but risk depends on exposure and controls
💧 Wet floors, medication mix-ups, and poor hand hygiene were discussed as everyday healthcare risks
Understanding this distinction helps healthcare professionals proactively reduce harm.
🏥 Common Patient Safety Issues
Several high-risk areas in healthcare were reviewed, including:
💊 Medication errors
🆔 Wrong patient identification
🤕 Patient falls
🛏️ Hospital-acquired pressure injuries
🦠 Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs)
Each was discussed in the context of prevention, reporting, and system improvement.
🧼 Infection Prevention & Hand Hygiene
A major focus was placed on infection prevention, including:
Central line-associated bloodstream infections
Ventilator-associated events
Surgical site infections
Catheter-associated urinary tract infections
The WHO’s 5 Moments of Hand Hygiene 🖐️ were reinforced as one of the simplest yet most effective ways to prevent infections and save lives.
💊 Safe Medication Practices
The session highlighted the Seven Rights of Medication Administration:
✔ Right patient
✔ Right medication
✔ Right dose
✔ Right route
✔ Right time
✔ Right documentation
✔ Right reason
These principles were presented as essential safeguards against medication-related harm.
🧠 Safety Systems and Reporting Culture
Healthcare safety was framed as a shared responsibility, supported by:
📋 Policies and procedures
💻 Electronic health records
📦 Barcode medication administration
👥 Competency assessments
The importance of incident reporting was emphasized, encouraging transparency and learning rather than blame—even when reputational or financial risks exist.
🎯 The Six Aims of Quality Improvement

Patient safety was aligned with the broader six aims of healthcare quality:
Safety
Effectiveness
Patient-centered care
Timeliness
Efficiency
Equity
The distinction between equality and equity was discussed, reinforcing the need to tailor care to individual patient needs.
🔍 Key Takeaways
✅ Most patient harm is preventable
✅ Systems, not individuals, are often the root cause
✅ Near misses are learning opportunities
✅ Strong safety culture saves lives
✅ Continuous improvement is essential
🚀 Moving Forward
Participants were encouraged to reflect on current practices in their workplaces, identify existing safety gaps, and actively contribute to a culture of learning, transparency, and patient-centered care. Continued discussions and assessments on patient safety are planned in upcoming sessions.
👉 Join our Free Demo Class and start your journey toward becoming a certified healthcare quality professional!
👉 Enroll in our Certified Professional in Healthcare Quality (CPHQ) preparation course to level up your career.
👉 Explore Now and start transforming your healthcare practice today