📊 "Data Without Limits: Exploring Power BI’s Ecosystem & Best Practices" 🌍✨
As organizations move toward data-driven decision-making, mastering tools like Power BI becomes essential. This session introduced the team to Power BI’s true potential, its limitations, and the right way to build reliable reporting systems. With participants joining from across the globe, the workshop also outlined the structure of the upcoming Power BI training program designed to take learners from beginner to professional level.
🚀 Power BI: What It Can and Cannot Do
The discussion opened with a clear understanding of Power BI's role in analytics:
✔️ What Power BI can do:
Build dynamic dashboards
Visualize KPIs for faster decisions
Connect to a wide range of data sources
Automate refreshes and analytics
❌ What Power BI is not:
A data warehouse
A large-scale storage platform
A substitute for systems like SQL, Snowflake, or SAP
The team emphasized that efficient reporting begins with clean data, clear KPIs, and proper sourcing.
⚙️ Why Excel Should Not Be Your Data Source
A key takeaway was understanding why organizations should avoid relying on Excel for operational reporting:
Excel is error-prone
Manual copying and updating leads to inconsistencies
It can't handle large, complex datasets
It breaks when templates change
Instead, Power BI should connect directly to ERP, DWH, CRM, SAP, or SQL to ensure automation, accuracy, and real-time decision-making.
🔗 Connecting Power BI to Real Data Sources
The team explored many systems that seamlessly integrate with Power BI:
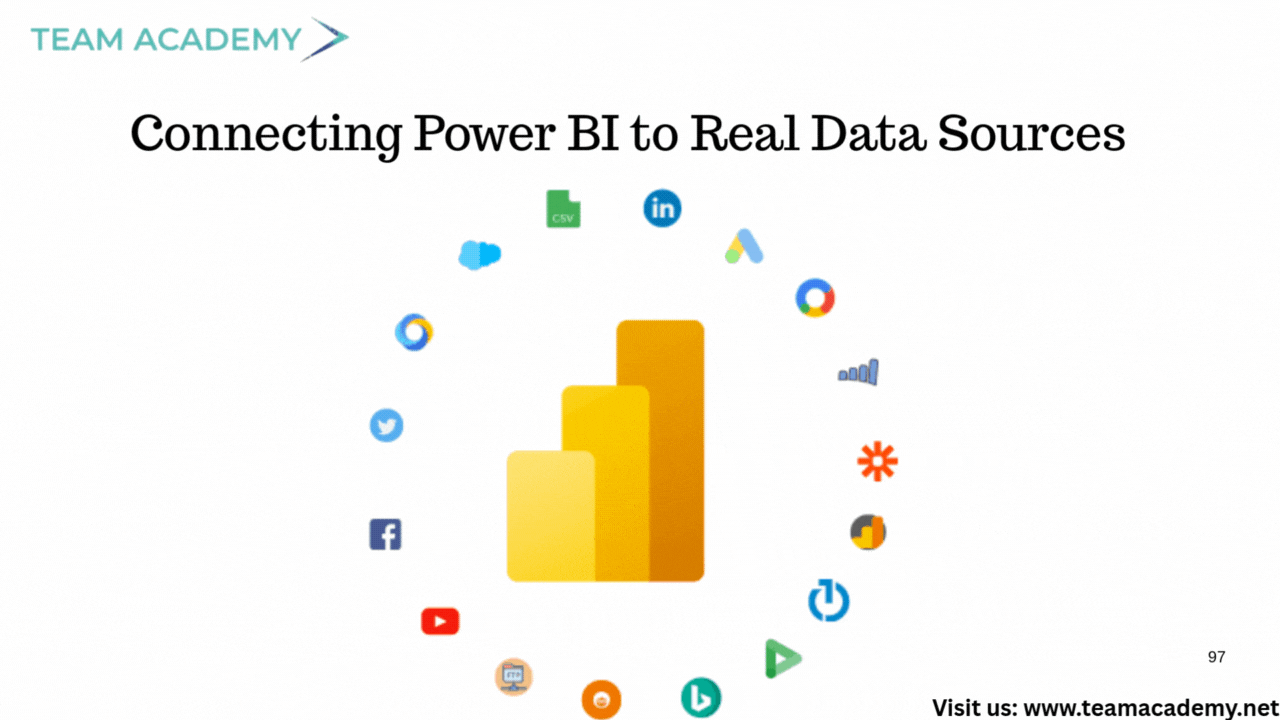
🗄️ Databases
SQL Server
Oracle
MySQL
IBM DB2
🌐 Online Services
SharePoint
Outlook
OneDrive
Fabric
☁️ External Platforms
Google Sheets
Smartsheet
ODataFeed / ODBC connectors
The message was clear:
👉 Power BI connects to almost everything — Excel is just for learning, not for enterprise reporting.
🧹 Data Transformation: Do It Right with Power Query
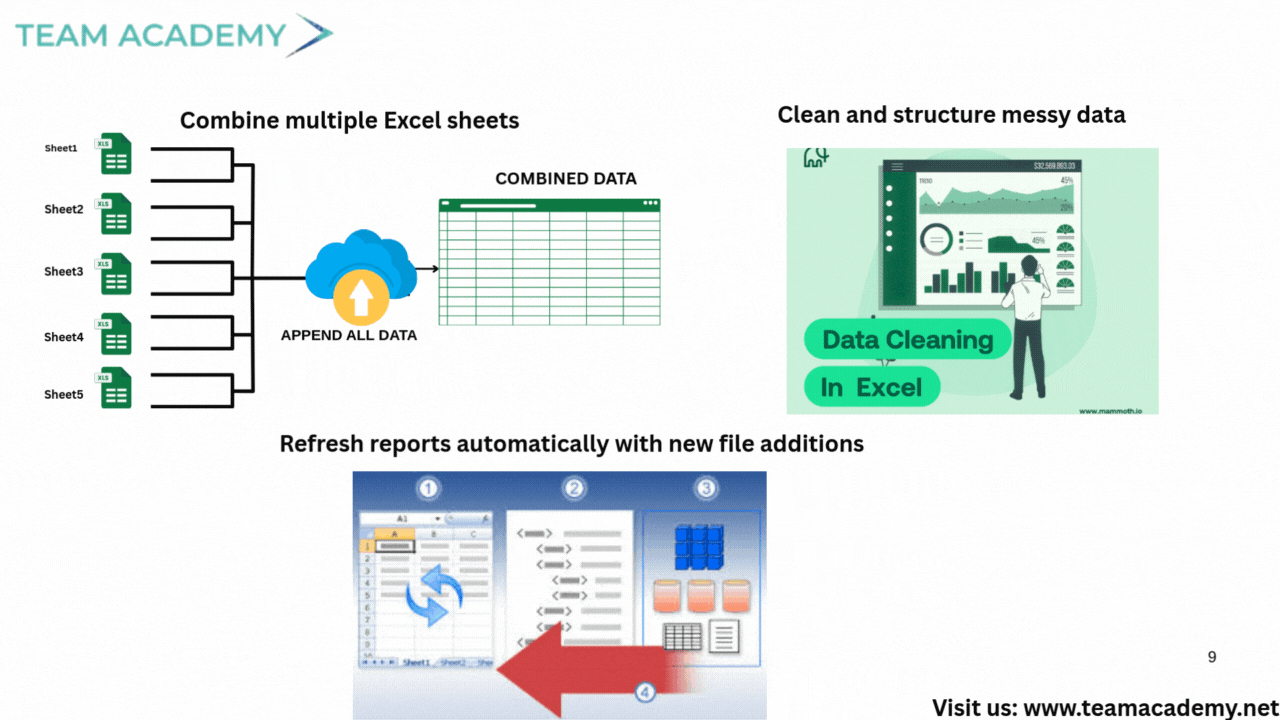
Participants learned how Power Query helps:
Clean messy data
Remove nulls
Consolidate sheets
Combine multiple files
Automate transformation steps
However, Power Query requires consistent templates — otherwise the logic breaks.
🧩 Understanding Power BI Modules
The core components of Power BI covered were:
1️⃣ Data Modeling
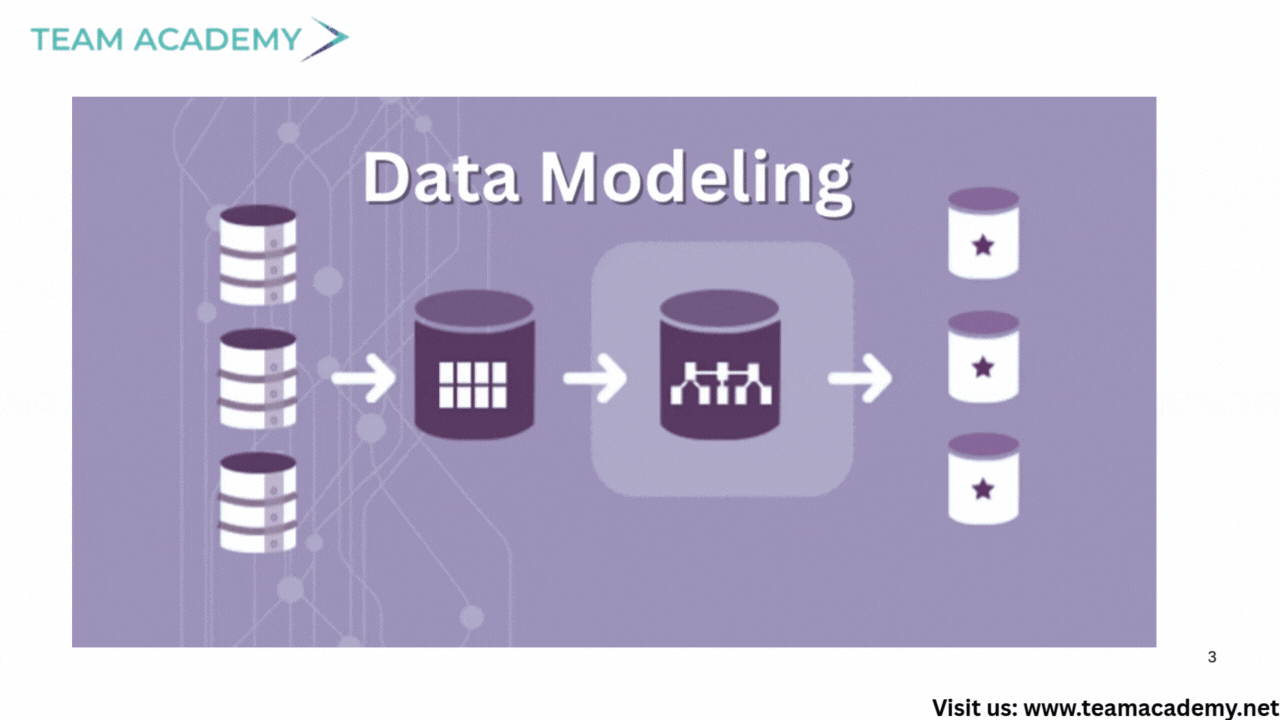
Establishing relationships between tables
Using identifiers like Product ID or Customer Number
Creating a single source of truth
2️⃣ Visualization
Building meaningful charts
Designing KPI dashboards
Managing filters & interactions
3️⃣ Fabric & Collaboration
Publishing reports
Sharing dashboards via Teams or websites
Setting up KPI alerts
The team discussed a real-world example of a catering company using IoT sensors and Power BI alerts to manage temperature monitoring.
🏗️ Training Program: What to Expect
The upcoming 1.5-month Power BI training covers:
Data collection
Data cleansing
Transformation
Modeling
Visualization
Collaboration & publishing
Learners must have:
Power BI installed
Datasets ready
A willingness to practice
Course sessions will blend theory + hands-on labs for professional-level mastery.