🚀 Agile Project Management Explained: A Practical Guide for PMP Aspirants 🧠
This session provided a comprehensive introduction to Agile Project Management, with a strong focus on Scrum as part of PMP exam preparation. Participants explored how Agile differs from traditional project management and learned how iterative delivery, collaboration, and continuous feedback drive successful project outcomes.
🔄 Agile vs Predictive Project Management
A key discussion point was the difference between predictive (Waterfall) and Agile lifecycles:
📐 Predictive projects have fixed scope, time, and cost
🔁 Agile projects fix time and cost while allowing scope to evolve
Agile emphasizes flexibility, early delivery, and responsiveness to change—making it ideal for projects with uncertainty or evolving requirements.
🧩 Core Agile Concepts & Frameworks
Participants were introduced to Agile frameworks such as:
Scrum
Kanban
Lean
Hybrid approaches
Agile teams are:
👥 Self-organized
🔧 Cross-functional
📏 Ideally 6–9 members (maximum 12)
Work is delivered in short sprints (up to 4 weeks), enabling frequent feedback and faster value delivery.
🔁 Incremental vs Iterative Delivery
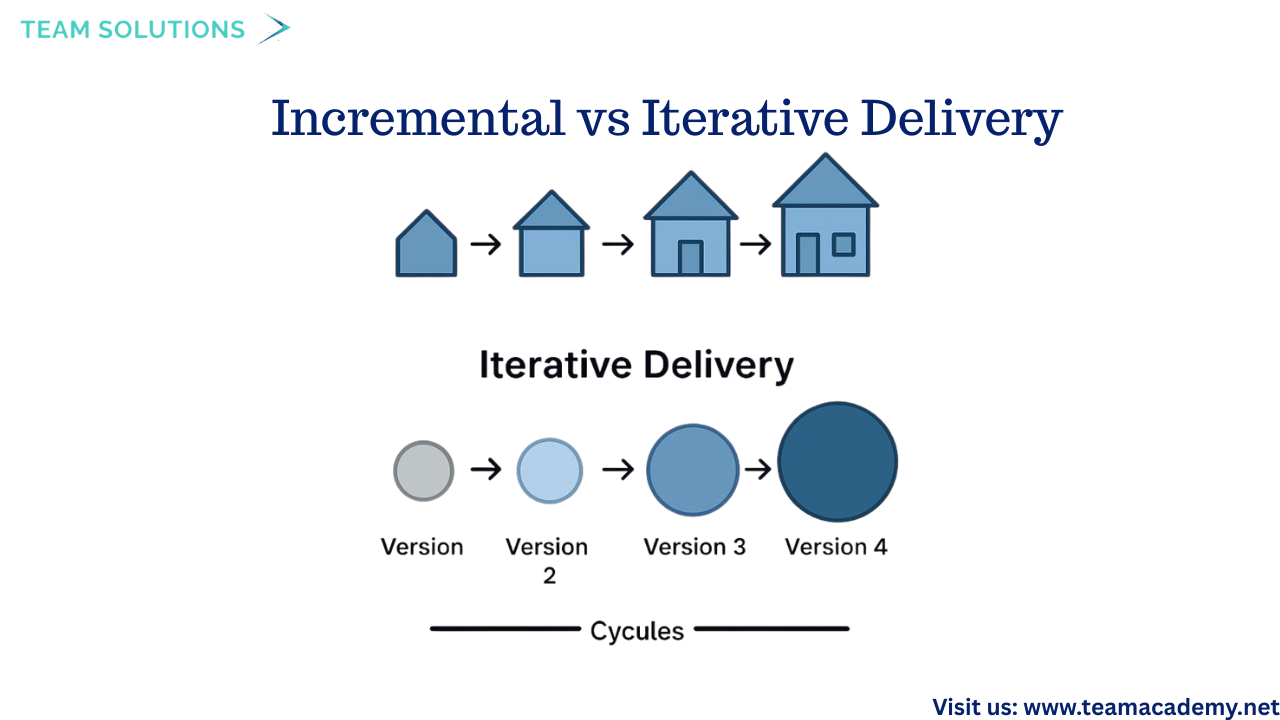
Two important Agile delivery approaches were explained:
➕ Incremental: Delivers usable parts of the product continuously
🔄 Iterative: Improves the product through repeated cycles
High-value items are always prioritized and delivered early to maximize stakeholder satisfaction.
💡 Agile Values & Principles
The session reviewed the 4 Agile Values:
👤 Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
💻 Working solutions over extensive documentation
🤝 Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
🔄 Responding to change over following a fixed plan
It also covered key Agile principles, including:
Early and continuous delivery
Embracing change
Frequent feedback
Sustainable pace
Continuous improvement through reflection
👥 Agile Roles & Responsibilities
Three key Scrum roles were discussed:
🎯 Product Owner – Manages the product backlog and maximizes business value
🛠️ Development Team – Builds and delivers the product increment
🧭 Scrum Master – Servant leader who facilitates Agile practices and removes obstacles
🗂️ Backlogs, User Stories & Planning
Participants learned how Agile work is organized using:
📋 Product Backlog – A dynamic list of prioritized user stories
📦 Sprint Backlog – Work committed by the team for a specific sprint
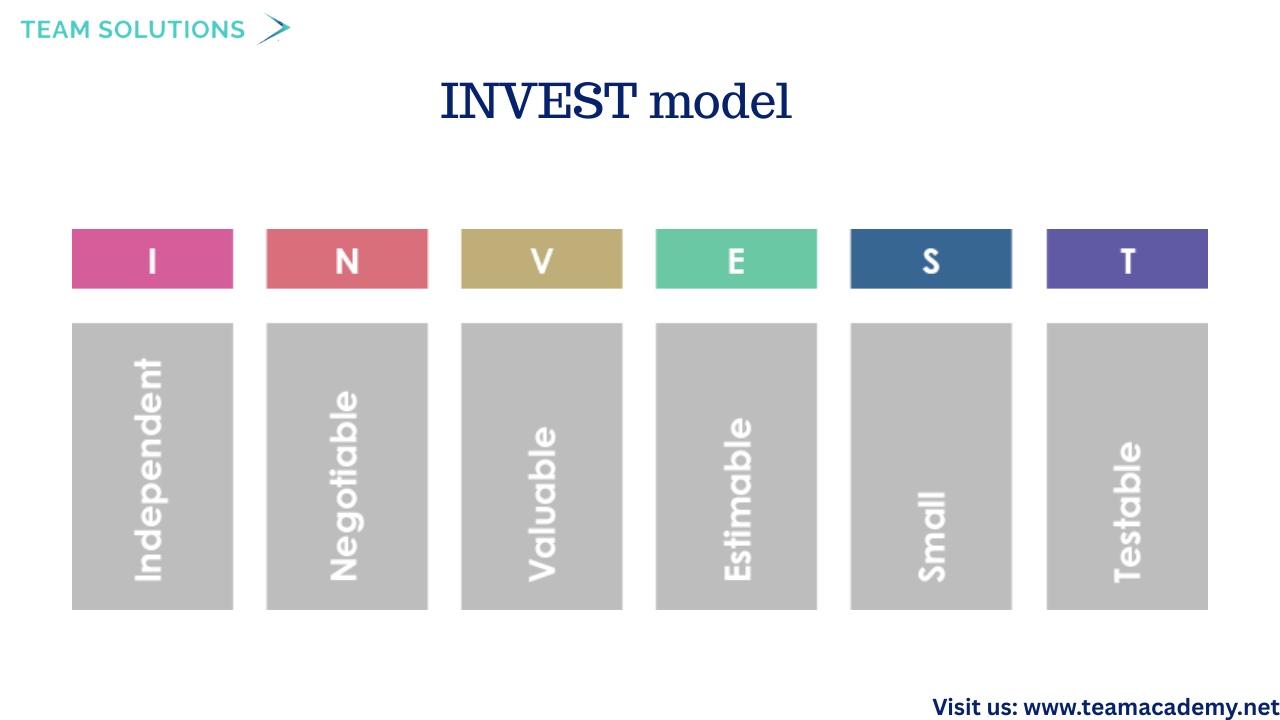
User stories follow:
✅ INVEST model
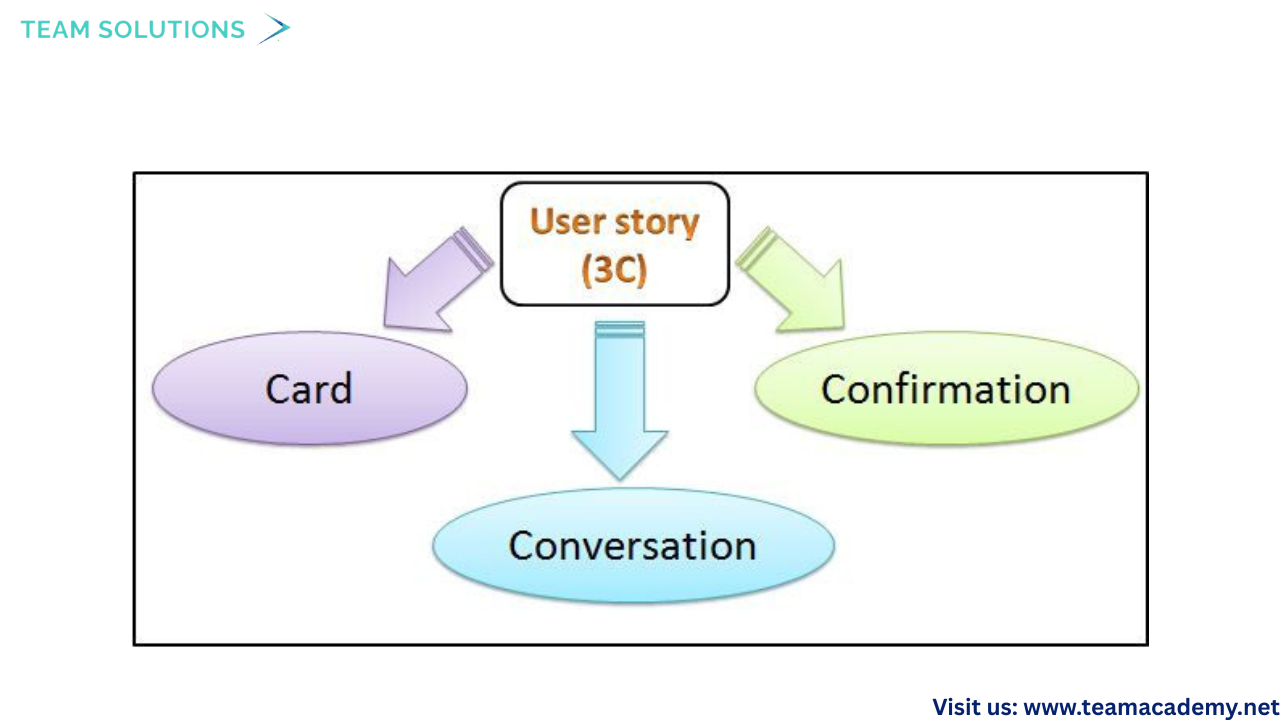
🧾 3Cs: Card, Conversation, Confirmation
🗓️ Scrum Events & Continuous Improvement
The four core Scrum events were explained:
🧠 Sprint Planning – Decide what to build next
⏱️ Daily Stand-up – 15-minute progress check
👀 Sprint Review – Demonstrate work and collect feedback
🔍 Sprint Retrospective – Improve processes and teamwork
The retrospective was highlighted as the key improvement event in Agile.
🗺️ Product Roadmap & Release Planning
Before creating the backlog, a product roadmap is developed to outline:
Release timelines
Business goals
High-level features
Agile release planning ensures alignment between stakeholders and delivery teams while allowing flexibility.
📊 Transparency & Information Radiators
Agile promotes transparency through:
📌 Information radiators
Visual boards
Real-time status updates
These tools help stakeholders track progress and support informed decision-making.
🎓 Key Takeaways for PMP Aspirants
Agile focuses on value, speed, and adaptability 🚀
Collaboration and feedback drive better outcomes 🤝
Understanding Agile concepts is essential for PMP success 🏆
Exam questions often mix Agile, predictive, and hybrid scenarios 🧠
This session provided a strong foundation in Agile thinking, helping participants connect theory with real-world project delivery and PMP exam expectations.
📌 Practice smart, think like a project manager, and success will follow!
👉 Join our Free Demo Class
👉 Enroll in our Project Management Programs to master predictive, Agile, and hybrid approaches.
👉 Explore now to deepen your skills and stay ahead in your career