📊 📈 Beyond EHRs: How Health Data Analytics Improves Care & Compliance🏥📈
In today’s data-driven healthcare environment, the effective use of health data analytics plays a critical role in improving patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. This session offered a comprehensive walkthrough of how healthcare data is collected, managed, protected, and analyzed—bridging theory with real-world application.
🖥️ Electronic Health Records (EHR): Benefits & Best Practices
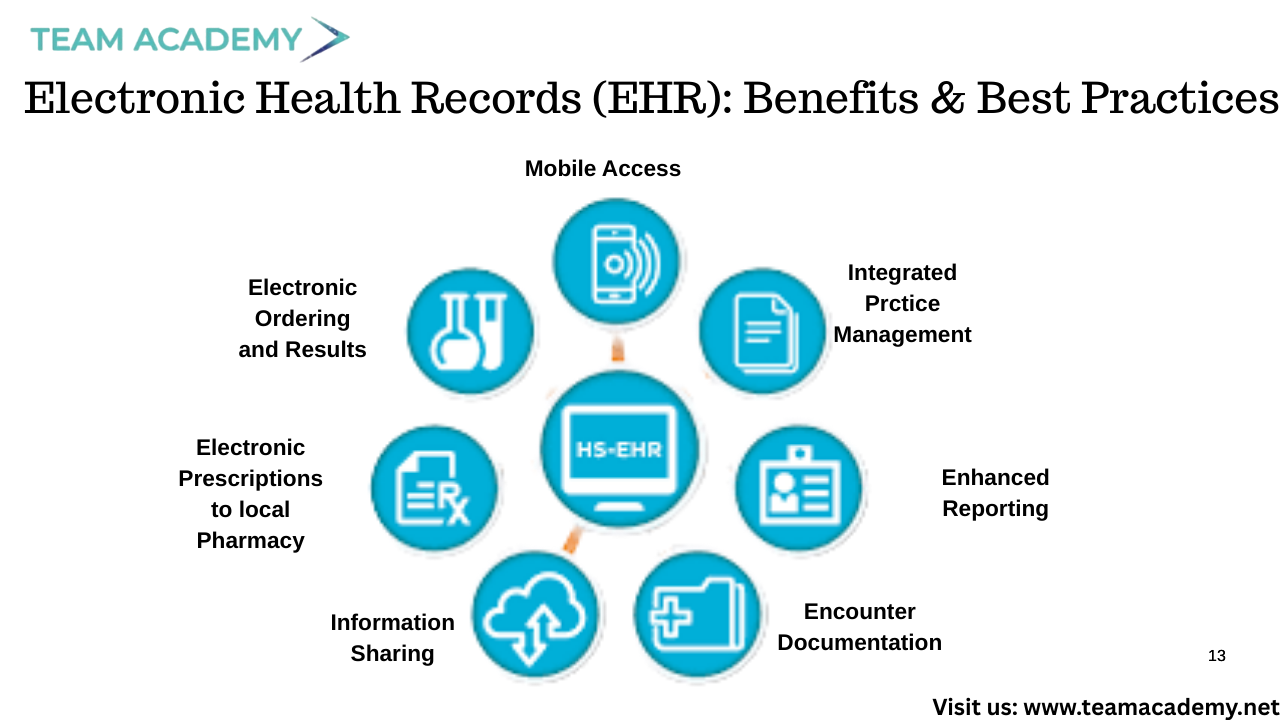
Electronic Health Records have transformed healthcare delivery by enabling:
✅ Faster and more accurate diagnoses
✅ Improved communication across care teams
✅ Reduced paperwork and administrative burden
✅ Better disease tracking and management
At the same time, the discussion emphasized that while EHRs reduce many risks, errors can still occur during medication administration. This highlights the need for strong clinical workflows and continuous monitoring.
🔐 Healthcare Data Security & Privacy
Protecting patient data is non-negotiable. Key best practices discussed included:
🔑 Unique user logins and multi-factor authentication
🖥️ Securing workstations and physical access areas
🗂️ Proper disposal of devices and paper records
🔒 Encrypted communication channels
🔄 Regular system updates, patches, and activity monitoring
The importance of regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA and the HITECH Act was highlighted to ensure compliance and trust in digital health systems.
📚 Health Data Management Fundamentals
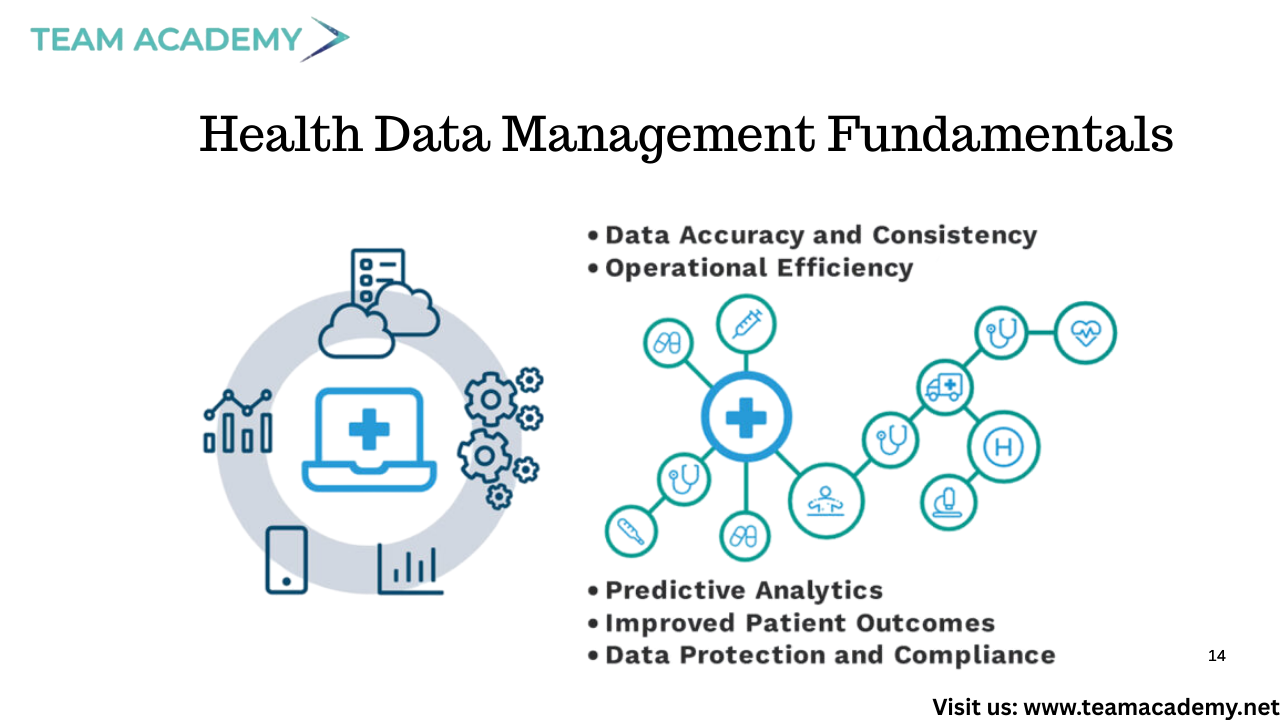
Effective data management relies on strong foundational principles:
Accuracy & consistency
Accessibility & timeliness
Clear definitions and standardized data
Comprehensive and reliable documentation
The session also explored risk adjustment, ensuring fair comparisons by accounting for patient complexity, and the role of evidence-based practices in healthcare decision-making.
📊 Understanding Data Types & Sampling Methods
Participants explored different types of healthcare data:
Categorical data (nominal & ordinal)
Continuous data (interval & ratio)
The discussion clarified that continuous data often provides greater statistical power due to its flexibility and precision.
Sampling methods were also covered in depth:
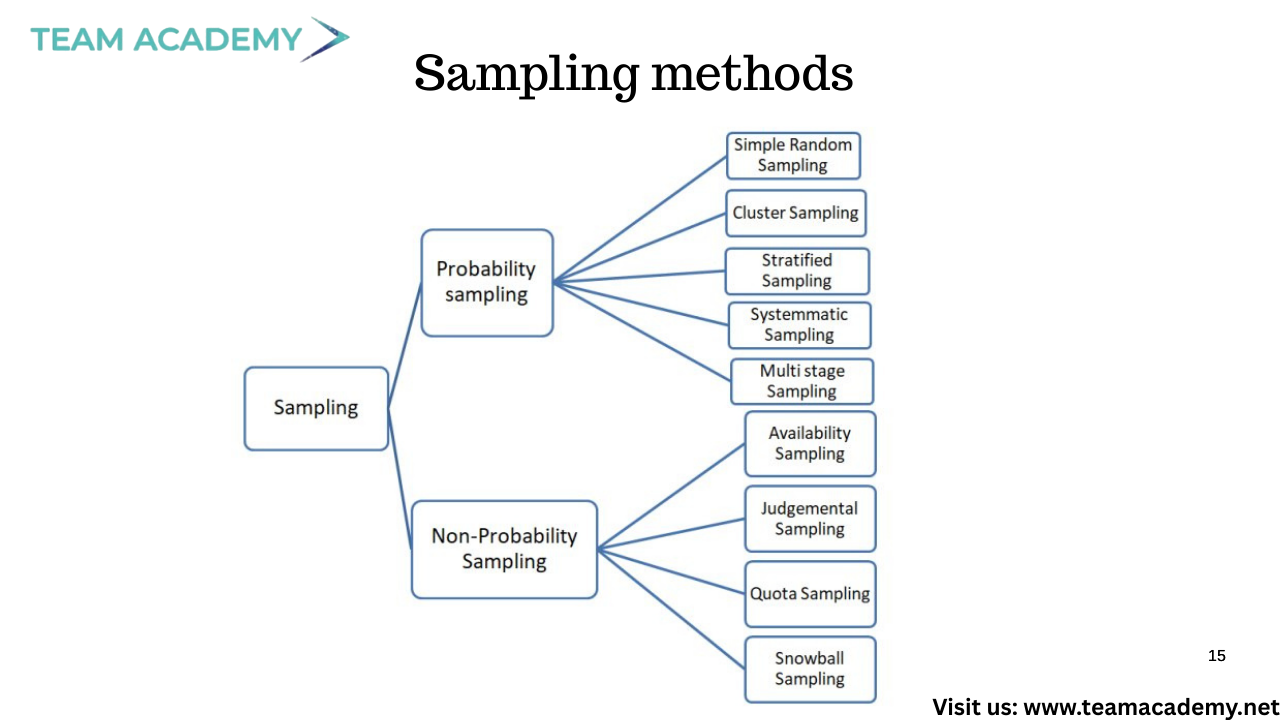
📌 Probability sampling: simple random, systematic, stratified, cluster
📌 Non-probability sampling: convenience, purposive, quota, snowball
📌 Data collection approaches: concurrent, retrospective, prospective
Each method’s strengths and limitations were reviewed with practical healthcare examples.
📐 Statistical Measures Made Simple
To turn data into insights, several statistical concepts were explained:
📉 Measures of central tendency: mean, median, mode
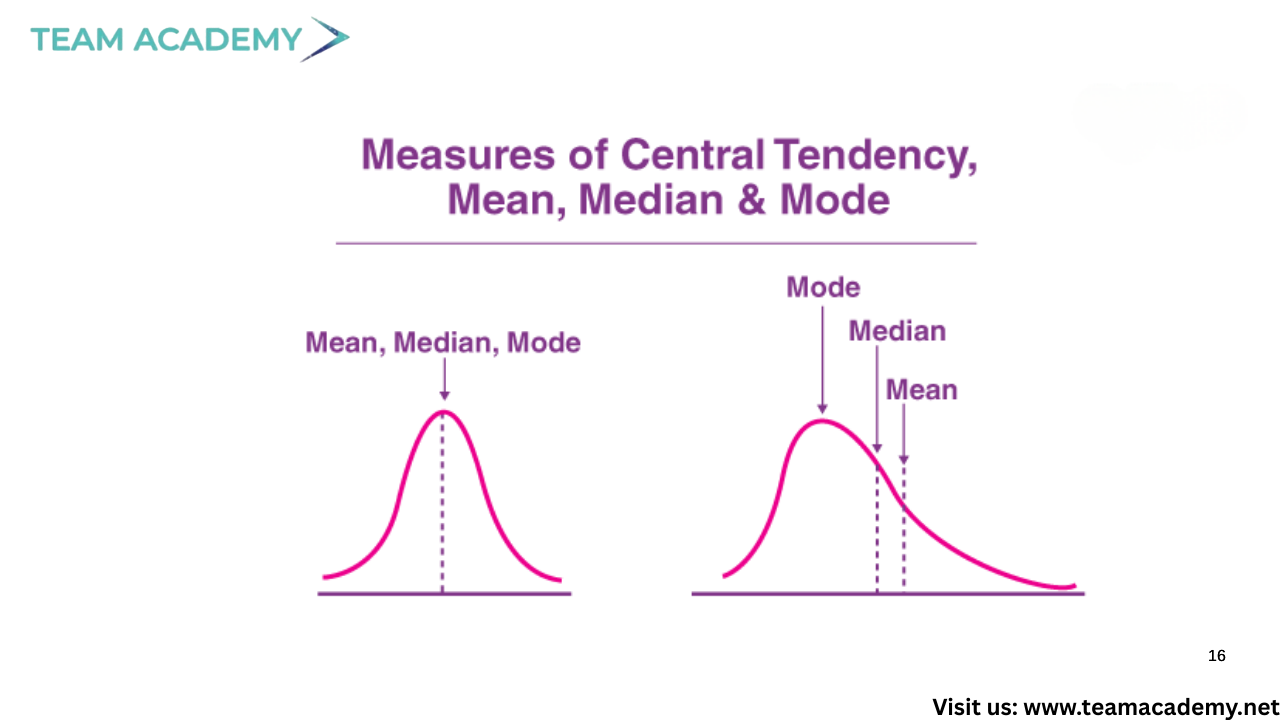
📏 Measures of variability: range and standard deviation
📊 Normal distribution and its use in clinical growth charts
Special focus was given to interpreting variation correctly and understanding how data spreads around the mean.
🧪 Hypothesis Testing & Clinical Decision-Making
The session concluded with an introduction to:
✅ Null and alternative hypotheses
✅ P-values and statistical significance
✅ Applying hypothesis testing in healthcare research and quality improvement
These concepts help healthcare professionals determine whether observed outcomes are meaningful or due to chance.
🌟 Key Takeaway
Health data analytics is more than numbers—it’s about secure data, sound methods, and meaningful interpretation. By mastering EHR practices, data management principles, sampling techniques, and basic statistics, healthcare professionals can make smarter, safer, and more impactful decisions.
📌 Stay curious, stay compliant, and keep transforming data into better care.
👉 Join our Free Demo Class and start your journey toward becoming a certified healthcare quality professional!
👉 Enroll in our Certified Professional in Healthcare Quality (CPHQ) preparation course to level up your career.
👉 Explore Now and start transforming your healthcare practice today